Intelligent networks for dynamic requirements
Agile management of WANs (Wide Area Networks) through software
SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) is a modern network technology which enables companies to manage their geographically dispersed WAN infrastructure via software. Unlike traditional WANs, which are based on fixed connection paths, SD-WAN uses a central control layer to dynamically route traffic across different network paths such as MPLS, broadband, 5G, or fiber optics.
How SD-WAN works
SD-WAN separates the control layer from the data layer, enabling intelligent, application-based prioritization of data traffic. The central management platform analyzes network conditions in real time and decides which path is best for which application.
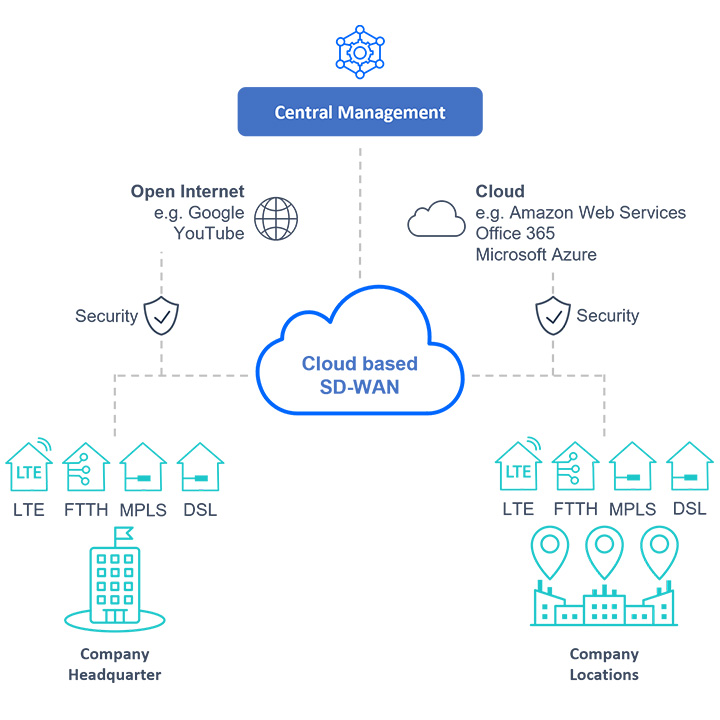
Function overview
- Central control of hardware elements, e.g. from the cloud (“overlay”)
- Management of physical network connections (“underlay”), e.g., fiber optic and mobile connections
- Control of data traffic according to customer-specific regulations and priorities
- Central distribution of configuration
- Real-time tracking
Benefits of SD-WAN
- Cost reduction: use of most cost efficient connections. MPLS can often be expensive
- Centralized management: uniform control of all locations, e.g., via a cloud-based platform
- Performance optimization: prioritization of business-critical applications
- Rapid response: to disruptions, outages, or capacity bottlenecks
- Security: integrated encryption, firewall functions, and zero trust solutions
- Scalability: rapid integration of new locations and cloud services
Optimized infrastructure and reduction of effort and costs
Networks can be more efficient with SD-WAN
Optimized infrastructure
Enhanced performance
Higher security
Easy management and monitoring
Reduction of effort and costs
General
- Hybrid networks: parallel use of MPLS, internet, and LTE connections
- Application-based routing: customer specific application SLAs for performance improvements
- Security: full encryption of all transmitted data, regardless of the transport medium
- Network segmentation: enables the separation of data streams through the implementation of different logical topologies
- Centralized management: provides a central control platform that enables homogeneous configurations
- Zero-touch provisioning: plug-and-play implementation of new SD-WAN devices
Management of applications
- SLA application recognition: An integrated Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) engine enables SD-WAN devices to recognize and control a wide range of applications
- Traffic engineering via dynamic path selection: The control layer works with a dynamic routing protocol and enables paths to be selected based on various specifications
- Performance-based routing: This feature prevents the use of paths that do not meet the application's SLA requirements and thus impair the user experience. Routing decisions can be based on SLA criteria such as packet loss, jitter, or latency
- Cloud connectivity: In addition to the ability to map local Internet breakouts, SD-WAN enables direct forwarding of a variety of cloud applications to the associated cloud servers
Foundation for digitalization of companies
- SD-WAN is a higher-level, software-based control and management entity for the physical network connections used in a distributed corporate network
- Significant reduction in complexity and costs through centralized and simple management of spatially distributed, heterogeneous network structures
- Proactive detection and resolution of capacity bottlenecks or impairments/outages in real time
- Fast and flexible response to changing business requirements (e.g. integration of new locations or suppliers)
- Basis for digitalization (e.g. cloud strategy)


SD-WAN offers versatile areas of application
SD-WAN is suitable for companies of all sizes and industries. Retailers can benefit from SD-WAN for highly reliable branch networking, while in healthcare it enables secure access to central patient records.
Financial service providers also benefit from the high security requirements and real-time communication. Industrial and manufacturing companies can use SD-WAN to connect their production sites and IoT devices.
Contact
For further information on our products, services, and business models, our experts are available via:
partnerschaften@telefonica.com

Marius Braun
Senior Business Development Manager